Principal Of Saving Energy Lighting Design
One of the most important aspects of saving energy lighting design is to determine the number of luminaires required, based on a given illuminance value. The room utilisation factor method is a sufficiently accurate and relatively simple procedure for finding the required number of luminaires (n):
![]()
Room utilisation factor method
1. Status of the saving energy lighting system
The planning factor takes into account the reduction in luminous flux and soiling of the light fittings. Planning factor = 1.25
2. Rated illuminance E
According to DIN 5035, Part 2 for the room in question, depending on the type of activity.
3. Room factor k
The room factor k makes allowance for the shape of the room:
![]()
a = Room width
b = Room length
H = Room height
h = H - 0.85 m
4. Luminous flux ![]()
Taken from the lamp catalogue, depending on the lamp to be used in the luminaire.
5. Luminaire efficiency ![]() LB
LB
Taken from the luminaire, depending on the luminaire selected.
6. Room utilisation factor ![]() R
R
From the LiTG table for the selected luminaire on the basis of the classification (e.g. A40.2). The effect of light distribution in the room is covered by the value from the appropriate table. Table 1 contains the room utilisation factor R as a percentage against the room factor (k), based on a combination of the reflectances of the ceilings, walls and work surfaces (or floors).
Basis:
reflectances ![]()
The reflective properties of the room surfaces are measured in terms of the reflectances of the ceilings, walls and work surfaces (or floors). Reflectances can be determined with the aid of reflectance tables.
|
Luminaries ceiling mounted Reflectances p |
||||||||||
| Ceiling | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| Wall | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Surface | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
|
Room factor k |
Room utilisation factor in % | |||||||||
| 0.6 | 73 | 46 | 37 | 44 | 36 | 66 | 36 | 42 | 35 | 35 |
| 0.8 | 82 | 57 | 47 | 54 | 46 | 74 | 45 | 51 | 44 | 44 |
| 1.0 | 91 | 66 | 56 | 62 | 54 | 80 | 53 | 59 | 52 | 51 |
| 1.25 | 98 | 75 | 65 | 70 | 62 | 85 | 61 | 66 | 60 | 59 |
| 1.5 | 103 | 82 | 73 | 76 | 69 | 89 | 67 | 72 | 66 | 65 |
| 2.0 | 109 | 91 | 82 | 84 | 78 | 94 | 75 | 78 | 73 | 72 |
| 2.5 | 114 | 98 | 90 | 90 | 84 | 97 | 81 | 83 | 79 | 77 |
| 3.0 | 117 | 103 | 96 | 95 | 90 | 99 | 86 | 87 | 83 | 82 |
| 4.0 | 120 | 109 | 103 | 100 | 95 | 101 | 91 | 91 | 88 | 86 |
| 5.0 | 122 | 113 | 107 | 103 | 98 | 103 | 93 | 93 | 91 | 89 |
Table 1:
This table shows the room utilisation factor for numerous combinations of room factors and reflectances (always assuming ideal dispersion). The illuminance E required in a room of area a x b is achieved with n luminaires that have an efficiency ![]() LB and with lamps with a luminous flux
LB and with lamps with a luminous flux ![]() .
.
Example:
Illumination of a conference room with 2X 24 W energy saving lamps.
Room dimensions
a = 15.00 m
b = 8.00 m
H = 3.40 m
h = 2.55 m
Required quality of light
Conference room:
light colour ww or nw,
R a group 2A
Illuminance
E = 300 Lux
Selected lamp
2 DULUX L 24 W,
light colour LUMILUX Warm
(LF 31/830), R a group 1B,
luminous flux per lamp
![]() = 1800 Lumen
= 1800 Lumen
Luminaire efficiency and light distribution
ESL 2 x 24 W
Light distribution A40.2 hLB = 0.58
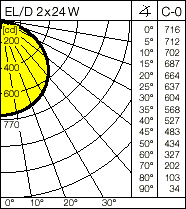
Reflectances
![]() Ceiling = 0.8
Ceiling = 0.8
![]() Wall = 0.5
Wall = 0.5
![]() Work surface = 0.3
Work surface = 0.3
Room utilisation factor
from the LiTG table
for A40.2 (Table 1)
![]() R = 0.91
R = 0.91
Calculation:
![]()
![]()
Result:
24 luminaires (n is rounded up)
Recommended arrangement:
3 rows of 8 luminairies.
